Assessing Value
In addition to pinpointing your organization's EHS&S challenges and considering hazard classifications like those from OSHA (Biological, Chemical, Ergonomic, Physical, Safety), a key step is to evaluate the value an EHS&S solution offers through proactive hazard resolution, continuous monitoring, and early problem prevention.
Ideal “To-Be” Scenario:
While the specific value of an EHS&S solution is unique to each organization, several generic value drivers are crucial to consider:
- Solution Requirements: Meeting the fundamental needs and expectations defined by the organization's specific challenges and identified hazards.
- Risk Mitigation Capabilities: The breadth of functions and the solution's ability to effectively address and mitigate identified risks.
- Reputation Protection: Maintaining the organization's reputation by preventing short- and long-term damage from hazards.
- Vendor Support: The quality of services and warranties provided by the EHS&S solution vendor.
- Vendor Trust: The level of trust and confidence in the vendor's ability to ensure mutual success.
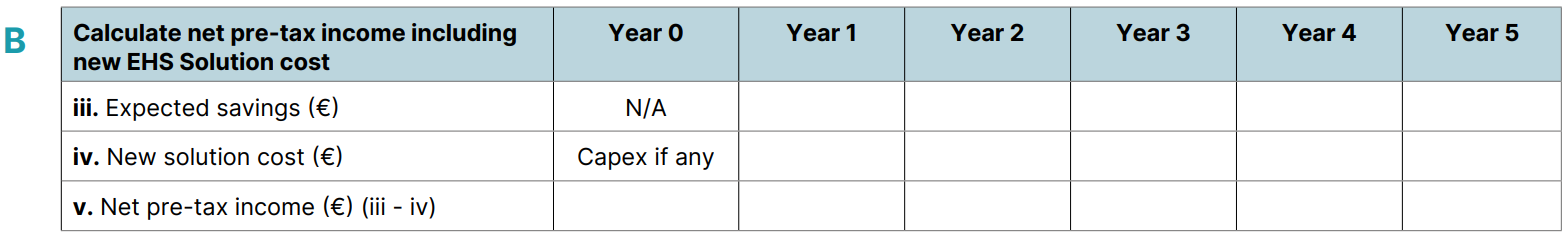
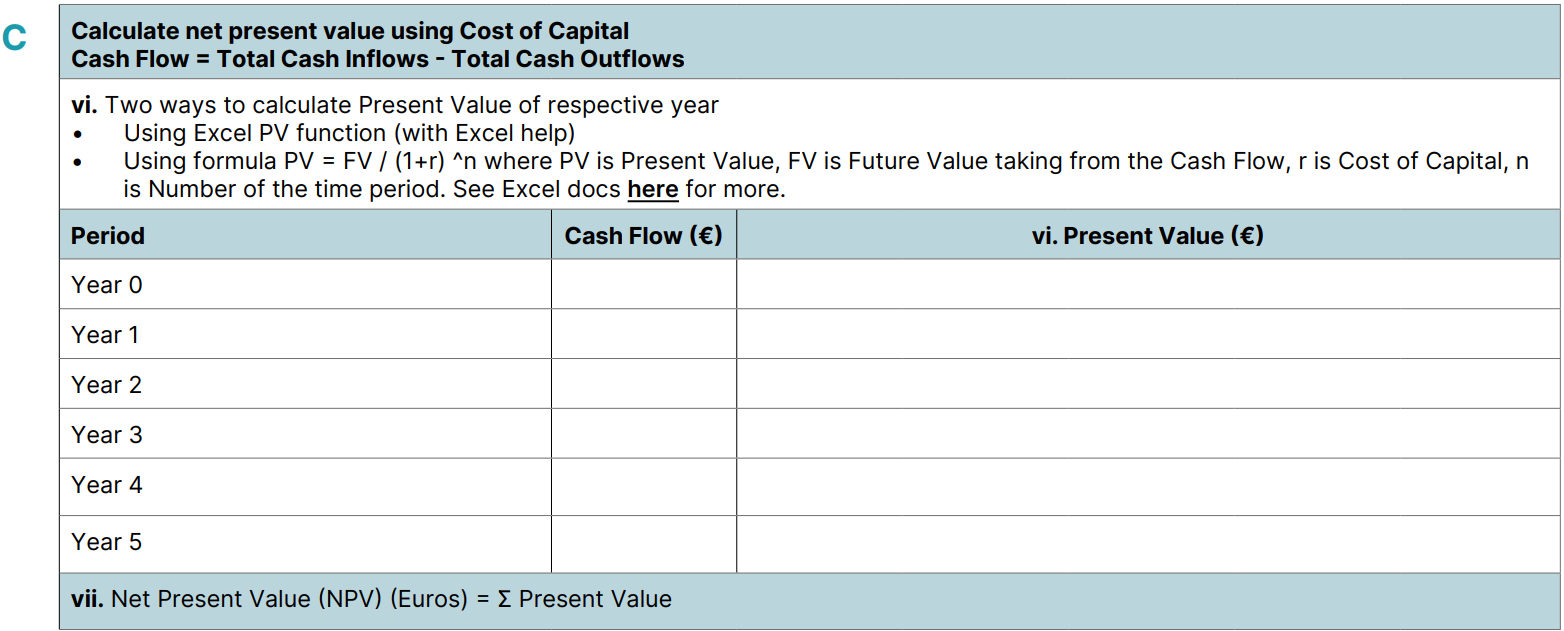
With these value drivers established, the next step is to define detailed business and technical requirements. This will enable us, as the EHS&S solution vendor, to determine the solution's cost, including implementation, hereafter referred to as 'New Solution Cost,' representing the estimated total cost of the new EHS&S solution and its added value.
Factual “As-is” Scenario:
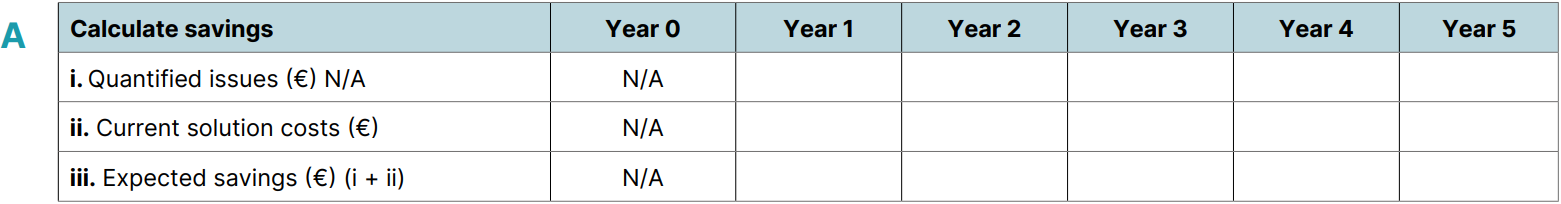
In addition to evaluating the new solution's cost, a comprehensive understanding of the financial consequences of the current situation is essential. Just as value drivers are organization-specific, so too are the financial aspects of EHS&S management.
- A critical step is to assess the cost of current EHS&S systems and processes, which may include tools like Excel or others.
- It's equally important to quantify the financial risks and losses stemming from current shortcomings. This goes beyond the Total Cost of Ownership to include the financial impact of:
- Inadequate incident management
- Increased vulnerability to non-compliance
- Negative effects of safety risks on employee engagement and retention
- Hazards arising from unplanned events
- Production delays attributable to EHS&S issues
- Loss of customer confidence due to perceived EHS&S risks
- Competitive disadvantage resulting from EHS&S deficiencies
- The totality of financial losses incurred due to these factors
By quantifying these costs, which we'll term 'Expected Savings,' we establish the financial baseline of current systems and processes. This baseline is crucial for determining the potential savings achievable with an improved EHS&S solution in the Ideal 'To-Be' Scenario."